Multi-signature blockchain technology
Implementing a joint authorization mechanism involving several cryptographic keys significantly elevates the protection of digital assets. By requiring a predefined threshold of independent signatures to validate transactions, this approach distributes control and mitigates risks associated with single points of failure. Such signature aggregation allows entities to enforce collaborative decision-making, ensuring that no individual keyholder can […]

Multi-signature wallets basics
Multiple keys distributed among different participants enhance security by preventing single-point control over digital assets. This joint approach requires a predefined threshold of key holders to grant approval, ensuring no unilateral actions can occur without consensus. Such a system minimizes risks related to compromised private keys or insider threats. The mechanism, often referred to as […]

Blockchain mempool dynamics
Analyzing the flow of transactions awaiting confirmation reveals critical patterns in how the transaction queue behaves under varying network conditions. The backlog of unconfirmed operations forms a temporary storage area where each item competes for processing based on assigned priority levels. Observing this layer provides insight into congestion points and efficiency bottlenecks that directly affect […]

Avoiding FOMO trading
Discipline is the cornerstone of successful market engagement. Reacting to fear-driven impulses often leads participants to enter positions hastily, driven by the anxiety of missing out on potential gains. Establishing a clear strategy before executing any position helps maintain objectivity and reduces the influence of sudden emotional surges. The sensation of being left out can […]
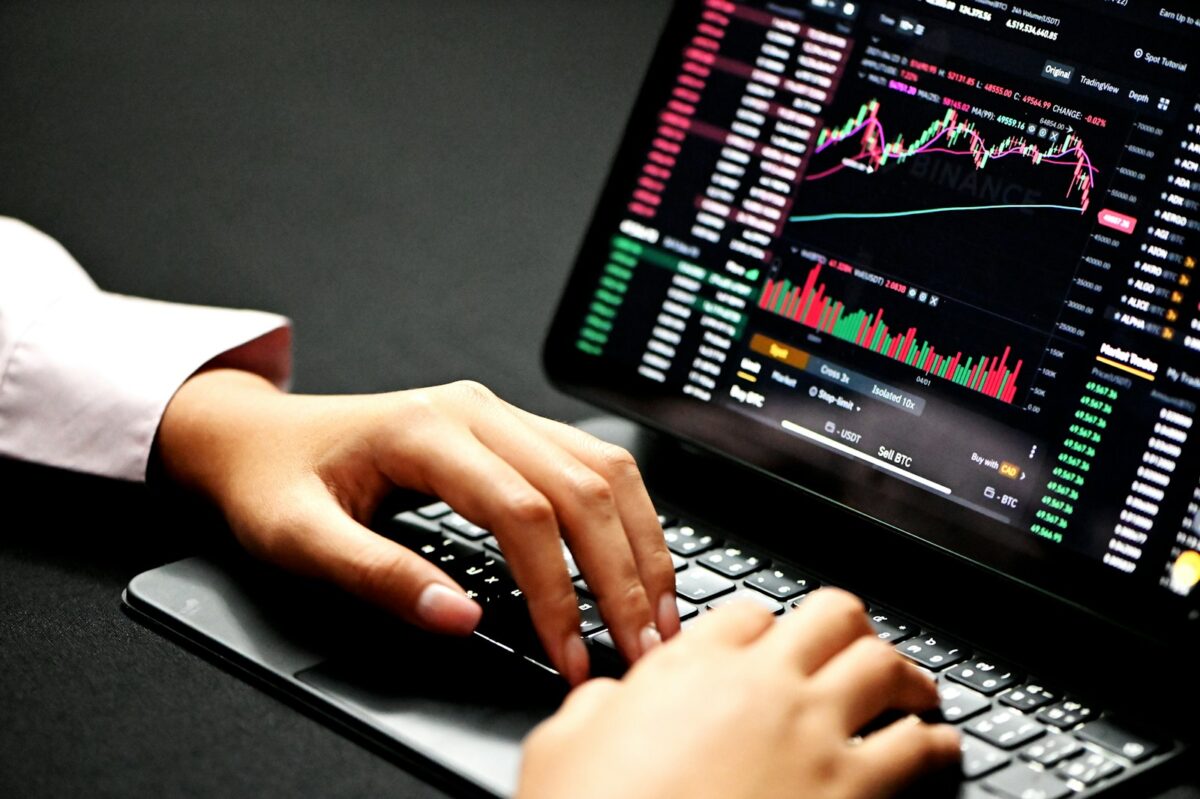

Reading cryptocurrency charts basics
Candlesticks represent discrete snapshots of price movement over specified time intervals, encapsulating open, high, low, and close values. Understanding their formation allows precise identification of market sentiment shifts and volatility spikes. Observing sequences of these shapes reveals recurring patterns, which serve as visual cues for potential trend reversals or continuations. Analyzing the interplay between price […]

Crypto community safety
Awareness of potential threats directly correlates with improved security measures among participants in decentralized platforms. Regular engagement in specialized forums provides a dynamic environment for exchanging insights on vulnerabilities and defense mechanisms, creating a foundation for collective vigilance. Systematic education initiatives tailored to recognize phishing attempts, social engineering tactics, and software exploits equip individuals with […]

Crypto meetups and events
Participating in local gatherings and large-scale conferences offers unparalleled opportunities for learning. Attendees gain hands-on experience by engaging in practical workshops tailored to emerging technologies and innovative applications. These sessions provide a structured environment to test hypotheses and refine technical skills under the guidance of seasoned experts. Networking within these communities cultivates relationships that extend […]

Bridge security risks
Implement multi-signature validation and continuous auditing to minimize vulnerabilities in cross-chain protocols. Due to the complexity of transferring assets across different blockchain networks, weak points often arise from insufficient consensus mechanisms or flawed smart contract code. These gaps increase exposure to unauthorized access and manipulation. Most incidents of asset loss occur due to exploits targeting […]

Insurance and crypto investing
Protection against financial loss is a fundamental aspect of managing risk in any portfolio that includes blockchain-based assets. Incorporating coverage for potential disability or unforeseen life events strengthens security, ensuring that investment strategies remain resilient despite personal hardships. Establishing such safeguards allows investors to maintain steady asset growth without jeopardizing long-term stability. Effective risk management […]

DAO governance learning
Engaging members through transparent decision-making mechanisms improves participation rates by up to 40%, as demonstrated in multiple decentralized communities. Implementing structured voting protocols aligned with clear proposal criteria enhances both accountability and trust among participants. Experiment with weighted voting models to balance influence between long-term contributors and newcomers, fostering inclusive democracy within the organization. Understanding […]